UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
Aquaculture in India: Prospects for Food Security
Last Updated
6th April, 2025
Date Published
6th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

Aquaculture is increasingly vital for global and national food security, with India playing a significant role as a leading producer. This summary, based on an article from The Hindu dated April 5, 2025, explores India’s aquaculture sector, focusing on prawn production, technological innovations, and its contributions to nutrition and economic growth. It provides insights into an industry critical for sustainable development and agricultural policy.
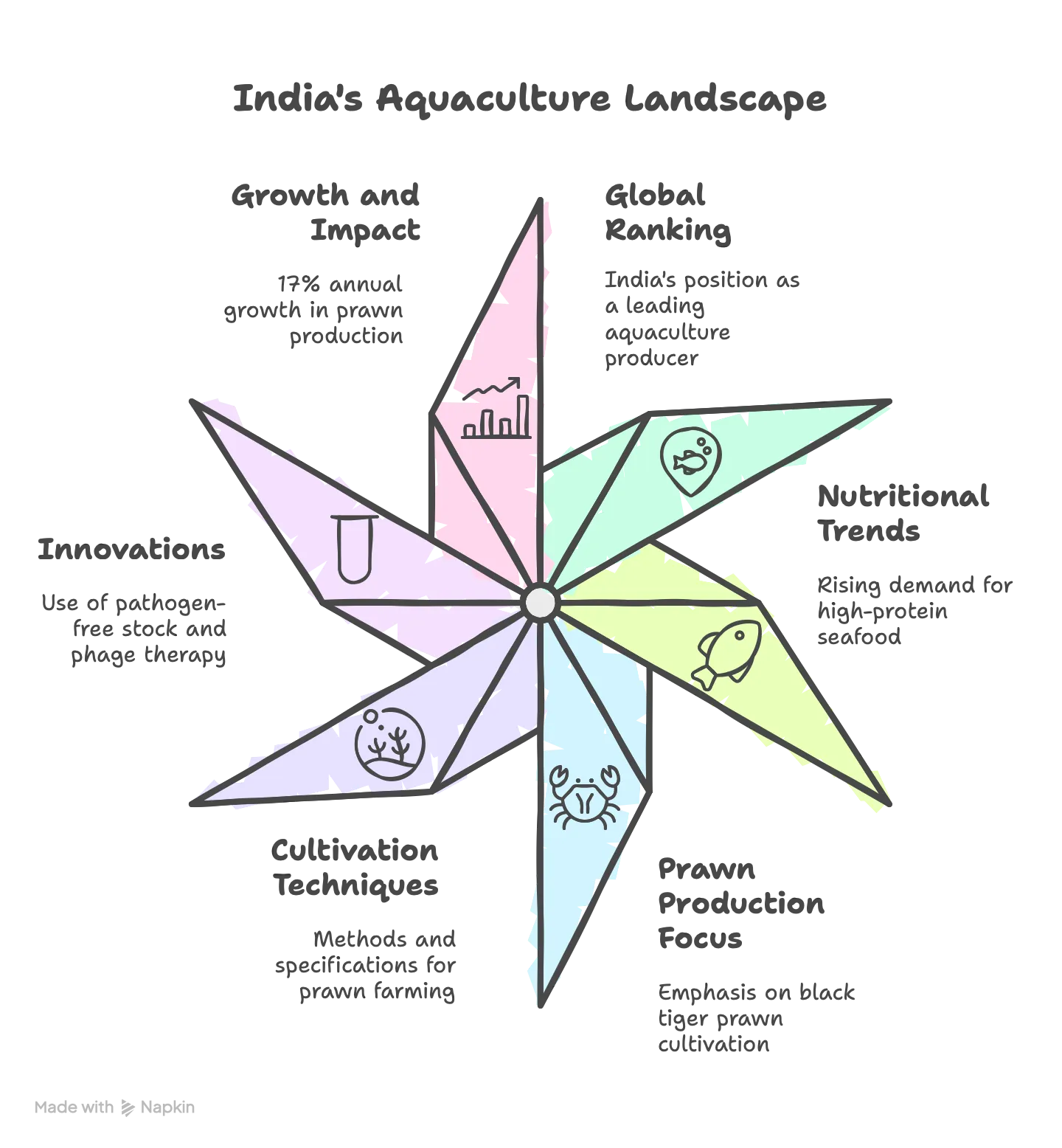
Key Points:
India’s Position in Global Aquaculture
- Ranking: India is the third-largest aquaculture producer globally and the second-largest in prawn production.
- Key States: Andhra Pradesh leads prawn production, followed by West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, and Gujarat.
Nutritional and Market Trends
- Dietary Shift: Rising demand for prawns domestically and in exports due to their high protein and low fat content.
- Economic Impact: Supported by industries supplying aquafeed, infection control, and other essentials.
Focus on Prawn Production
- Species: Black tiger prawn (Penaeus monodon) is a high-value marine species targeted for its market demand.
- Market Standard: Farmers aim for prawns weighing 30 or fewer per kilogram to meet premium market needs.
Cultivation Techniques
- Pond Specifications: Typical ponds measure 150 x 100 meters with a 2-meter depth.
- Salinity Requirements: Prawns need 10-25 grams of salt per liter (compared to seawater’s 35 grams/liter).
- Water Management:
- In Midnapore (West Bengal), seawater is brought in during high tides for low-lying farms.
- In coastal Andhra Pradesh, brackish groundwater is pumped and mixed with fresh river/canal water.
Innovations in Production
- Juvenile Prawns: Nursery-reared juveniles are used as starters, enhancing cultivation efficiency.
- Pathogen-Free Stock: The Central Institute of Brackishwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIBA) in Chennai develops ‘specific pathogen-free’ broodstock in biosecure facilities, certified free of high-risk pathogens.
- Phage Therapy: Bacteriophages targeting Vibrio bacteria are employed as an infection control measure, using viruses to kill harmful bacteria.
Growth and Impact
- Production Increase: These measures have driven a 17% annual growth rate in India’s prawn production.
- Collaborative Effort: Growth reflects contributions from field-experienced farmers and research-driven initiatives.
Contributors
- Authorship: Article by D. Balasubramanian, with collaboration from Sushil Chandani, a molecular modeling expert.
Key Terms:
- Aquaculture: Farming of aquatic organisms like fish and prawns for food production.
- Black Tiger Prawn: Penaeus monodon - A high-value prawn species prized in markets.
- Salinity: Salt concentration in water, critical for prawn cultivation.
- Pathogen-Free Broodstock: Breeding stock certified free of specific disease-causing agents.
- Phage Therapy: Use of bacteriophages to combat bacterial infections in aquaculture.
- ICAR-CIBA: Central Institute of Brackishwater Aquaculture - A leading research body under ICAR.
- Bacteriophages: Viruses that infect and destroy bacteria, used in infection control.
- Aqua feed: Specialised feed for aquatic species to support growth and health.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/aquaculture-for-feeding-the-world/article69413034.ece