BIMSTEC vs. SAARC: Regional Cooperation Dynamics
Last Updated
5th April, 2025
Date Published
5th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

As Prime Minister Narendra Modi attends the 6th BIMSTEC Summit in Thailand on April 4, 2025, the spotlight falls on the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) and its comparison with the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC). This analysis, published in The Indian Express on April 4, 2025, explores their roles, challenges, and significance in India’s foreign policy, offering critical insights for aspirants preparing for competitive examinations focusing on international relations and regional groupings.
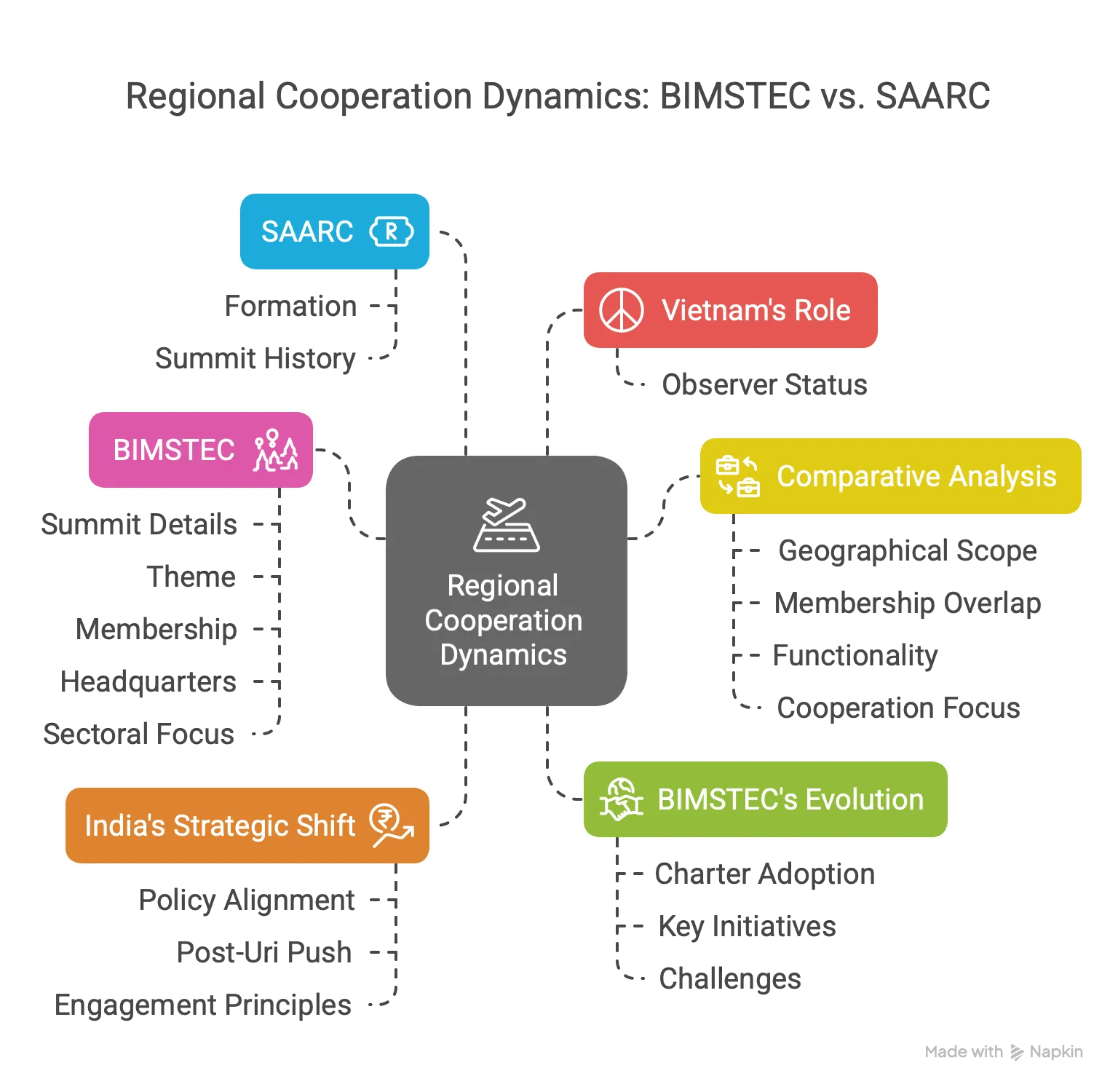
Key Points:
BIMSTEC Overview:
- Summit Details: The 6th BIMSTEC Summit, held in Bangkok, Thailand, on April 4, 2025, is the first physical meeting of leaders since the 4th Summit in Kathmandu (2018), following a virtual 5th Summit in Colombo (2022).
- Theme: “Prosperous, Resilient, and Open BIMSTEC (PRO BIMSTEC)” emphasizes economic growth, resilience, and openness.
- Membership: Comprises seven nations—Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka (South Asia), and Myanmar, Thailand (Southeast Asia)—formed on June 6, 1997, via the Bangkok Declaration.
- Headquarters: Located in Dhaka, Bangladesh, with Indra Mani Pandey (India) as the current Secretary General since 2020.
- Sectoral Focus: Initially covered six sectors (trade, technology, energy, transport, tourism, fisheries) in 1997, expanded to 14 in 2008, reorganized in 2021 with India leading security, counter-terrorism, transnational crime, disaster management, and energy.
SAARC Overview:
- Formation: Established in 1985 with eight members—India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Afghanistan—headquartered in Kathmandu, Nepal.
- Summit History: Held 18 summits in 39 years, with the last in Kathmandu (2014); the 19th, planned for Pakistan in 2016, was canceled after India’s boycott post-Uri attack.
Comparative Analysis:
- Geographical Scope: SAARC is a South Asian entity, while BIMSTEC bridges South Asia and Southeast Asia, connecting Himalayan and Bay of Bengal ecologies.
- Membership Overlap: Five SAARC members (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka) are in BIMSTEC; Pakistan’s absence in BIMSTEC avoids bilateral tensions.
- Functionality: SAARC is stalled due to India-Pakistan rivalry, notably after the 2014 summit failure, while BIMSTEC gained traction post-2016 Uri attack as India’s alternative platform.
- Cooperation Focus: BIMSTEC’s sector-driven approach contrasts with SAARC’s broader, less effective regional integration efforts.
India’s Strategic Shift:
- Policy Alignment: BIMSTEC supports India’s Neighbourhood First, Act East, and Northeast development policies, countering China’s Belt and Road Initiative influence.
- Post-Uri Push: India revived BIMSTEC in 2016, hosting an outreach summit alongside BRICS in Goa, signaling a shift from SAARC.
- Engagement Principles: India’s Ministry of External Affairs emphasizes consultative, non-reciprocal, outcome-oriented engagement with BIMSTEC nations, guided by “4Ss”—Samman (respect), Samvad (dialogue), Shanti (peace), Samriddhi (prosperity).
Vietnam’s Role:
- Observer Status: Vietnam attends the 6th BIMSTEC Summit as an observer, reflecting BIMSTEC’s openness to new members or observers, unlike SAARC’s rigid structure.
Beyond the Nugget: BIMSTEC’s Evolution:
- Charter Adoption: The BIMSTEC Charter, effective since May 20, 2024, grants legal personality, enhancing its diplomatic and operational framework.
- Key Initiatives: Includes the BIMSTEC Centre for Weather and Climate (India), Technology Transfer Facility (Sri Lanka), and Bangkok Vision 2030 for a sustainable Bay of Bengal region.
- Challenges: Inconsistent meetings (only five summits in 20+ years until 2022), broad focus areas, and pending Free Trade Agreement (FTA) talks since 2004 hinder progress.
Significance for India:
- Regional Influence: BIMSTEC offers India a platform to engage neighbors without Pakistan’s obstruction, enhancing connectivity and countering China’s regional dominance.
- Historical Context: C. Raja Mohan notes BIMSTEC’s image as a SAARC alternative emerged post-2014, reflecting India’s strategic pivot amid SAARC’s stagnation.
Glossary
- BIMSTEC: Regional organization linking South and Southeast Asia for technical and economic cooperation.
- SAARC: South Asian inter-governmental body for regional cooperation, stalled by India-Pakistan tensions.
- Bangkok Declaration: 1997 agreement establishing BIMSTEC.
- Neighbourhood First: India’s policy prioritizing relations with immediate neighbors.
- Act East: India’s strategy to strengthen ties with Southeast Asia.
- Uri Attack: 2016 terrorist attack prompting India’s SAARC boycott and BIMSTEC focus.
- Charter: Legal framework giving BIMSTEC international recognition and structure.
- FTA: Free Trade Agreement, a pending goal for BIMSTEC economic integration.
Link To The Original Article – https://indianexpress.com/article/upsc-current-affairs/upsc-essentials/knowledge-nugget-bimstec-saarc-upsc-vietnam-6th-prelims-9922446/