UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
Bommayapalayam Canyon: Tamil Nadu’s Geo-Heritage Treasure
Last Updated
11th April, 2025
Date Published
11th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

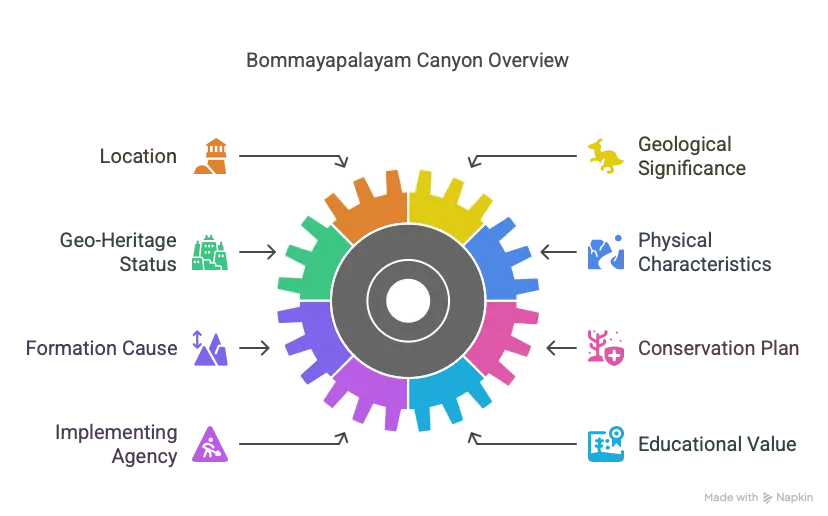
- Location: Bommayapalayam Canyon is situated in Vanur taluk, Villupuram district, Tamil Nadu.
- Geological Significance: A Miocene-age ravine (23.03 to 5.33 million years old), it serves as a repository of centuries of geological data.
- Geo-Heritage Status: Declared a geo-heritage site by the Tamil Nadu government to preserve its scientific value.
- Physical Characteristics: The canyon is a narrow, deep valley with steep sides, averaging 7 meters in height and 30 meters in width, characterized by reddish earth.
- Formation Cause: Result of prolonged soil erosion, not tectonic activity, as per soil conservationist Deepika Kundaji.
- Conservation Plan: The Tamil Nadu government announced a protection plan to maintain the canyon and enhance understanding of geological processes.
- Proposal Timeline: Initiated in May 2022 by the then Villupuram Collector to the Commissioner of Geology and Mining, recommending protection and maintenance.
- Implementing Agency: The Public Works Department will execute the conservation plan.
- Inspection Details: A preliminary inspection was conducted by a team led by the Regional Joint Director of Geology and Mining.
- Future Steps: A detailed proposal will be submitted to the government through the Commissioner of Geology and Mining in Chennai.
- Educational Value: The site aims to foster learning about dynamic geological processes among students and scientists.
- Funding: ₹5 crore allocated for protection and development to support research by geologists and scientists.
- Environmental Context: The canyon’s preservation highlights the importance of conserving natural formations for studying environmental history.
Glossary:
- Geo-Heritage Site: A location with significant geological features preserved for scientific and educational purposes.
- Miocene Age: A geological epoch from 23.03 to 5.33 million years ago, part of the Neogene period.
- Ravine: A narrow, deep valley with steep sides, typically formed by erosion.
- Soil Erosion: The wearing away of topsoil by natural forces like water or wind.
- Geological Processes: Natural mechanisms, such as erosion or sedimentation, shaping Earth’s structure over time.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/tamil-nadu/a-miocene-age-canyon-in-villupuram-is-a-repository-of-centuries-of-geological-data/article69434714.ece