On This Day Today
Civil Rights Act of 1968 Was Signed
Last Updated
10th April, 2025
Date Published
10th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

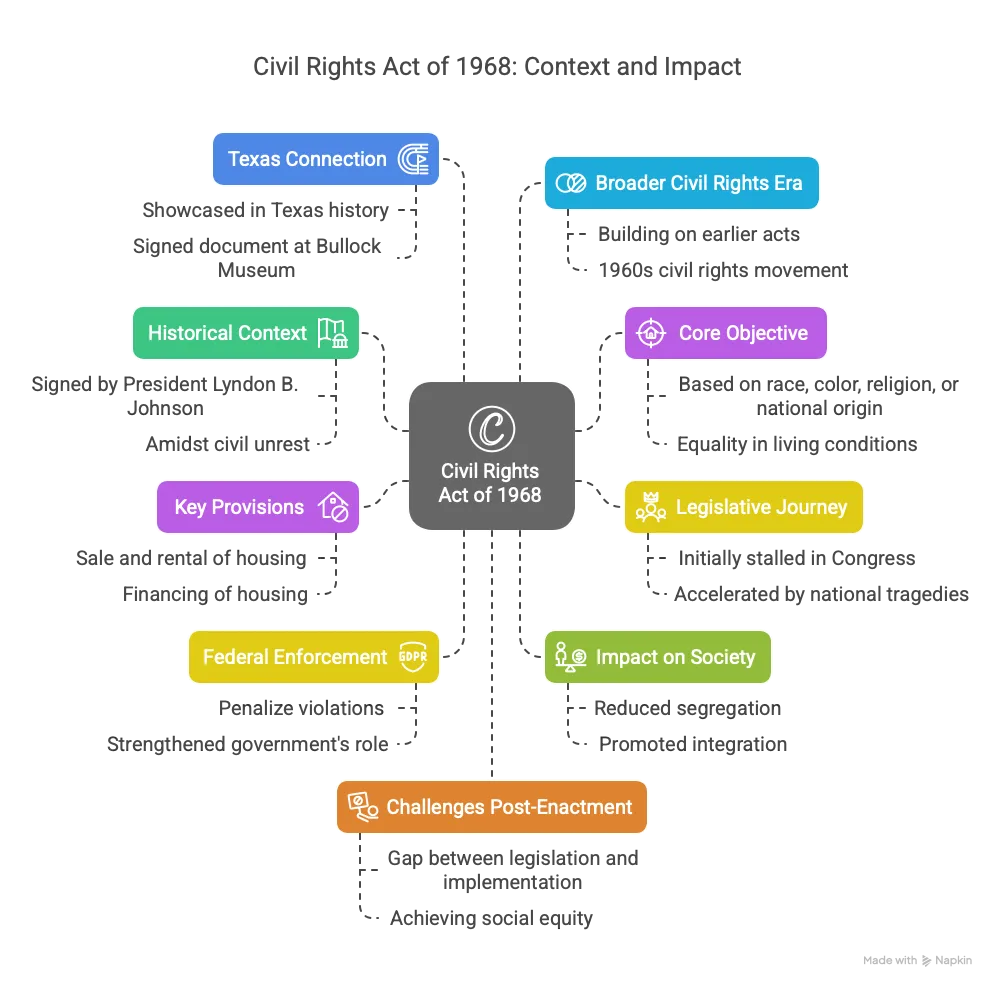
- Historical Context: Signed into law on April 11, 1968, by President Lyndon B. Johnson, the Civil Rights Act of 1968 was a landmark legislation addressing racial discrimination in the United States, enacted amidst civil unrest following Martin Luther King Jr.'s assassination.
- Core Objective: Known as the Fair Housing Act, it aimed to eliminate discrimination in housing based on race, color, religion, or national origin, marking a significant step toward equality in living conditions.
- Legislative Journey: Initially stalled in Congress, the bill gained momentum after King’s death, reflecting how national tragedies can accelerate legislative action on social justice issues.
- Key Provisions: It prohibited discriminatory practices in the sale, rental, and financing of housing, ensuring broader access to residential opportunities for minorities.
- Federal Enforcement: The Act empowered federal authorities to penalize violations, strengthening the government's role in upholding civil rights through legal mechanisms.
- Impact on Society: It addressed systemic inequalities in urban and suburban housing, reducing segregation and promoting integration in American communities.
- Texas Connection: As Johnson was a Texan, the Act is a point of pride in Texas history, showcased in artifacts like the signed document at the Bullock Texas State History Museum.
- Broader Civil Rights Era: It was the last major civil rights law of the 1960s, building on earlier acts like the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
- Challenges Post-Enactment: Despite its passage, enforcement faced resistance, highlighting the gap between legislation and practical implementation in achieving social equity.
- Global Relevance: The Act serves as a case study in balancing individual rights with societal reform, offering lessons in governance, law, and social policy for democratic nations.
Glossary
- Fair Housing Act: Another name for the Civil Rights Act of 1968, focusing on housing equality.
- Discrimination: Unfair treatment based on race, religion, or other traits.
- Segregation: The practice of separating groups, often racially, in living or social spaces.
- Legislation: Laws enacted by a governing body.
- Enforcement: The act of ensuring compliance with laws or rules.