UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
CRISPR-Based Diagnostics: Revolutionising Cancer Detection
Last Updated
6th April, 2025
Date Published
6th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

Advancements in medical technology are critical for addressing public health challenges, particularly in a country like India with a rising disease burden. The development of a CRISPR-based test for detecting rare blood cancers, as reported in The Hindu on April 5, 2025, showcases India’s growing contribution to global health innovation. This summary highlights key details of the RAPID-CRISPR test, its significance, and implications for healthcare accessibility and policy.
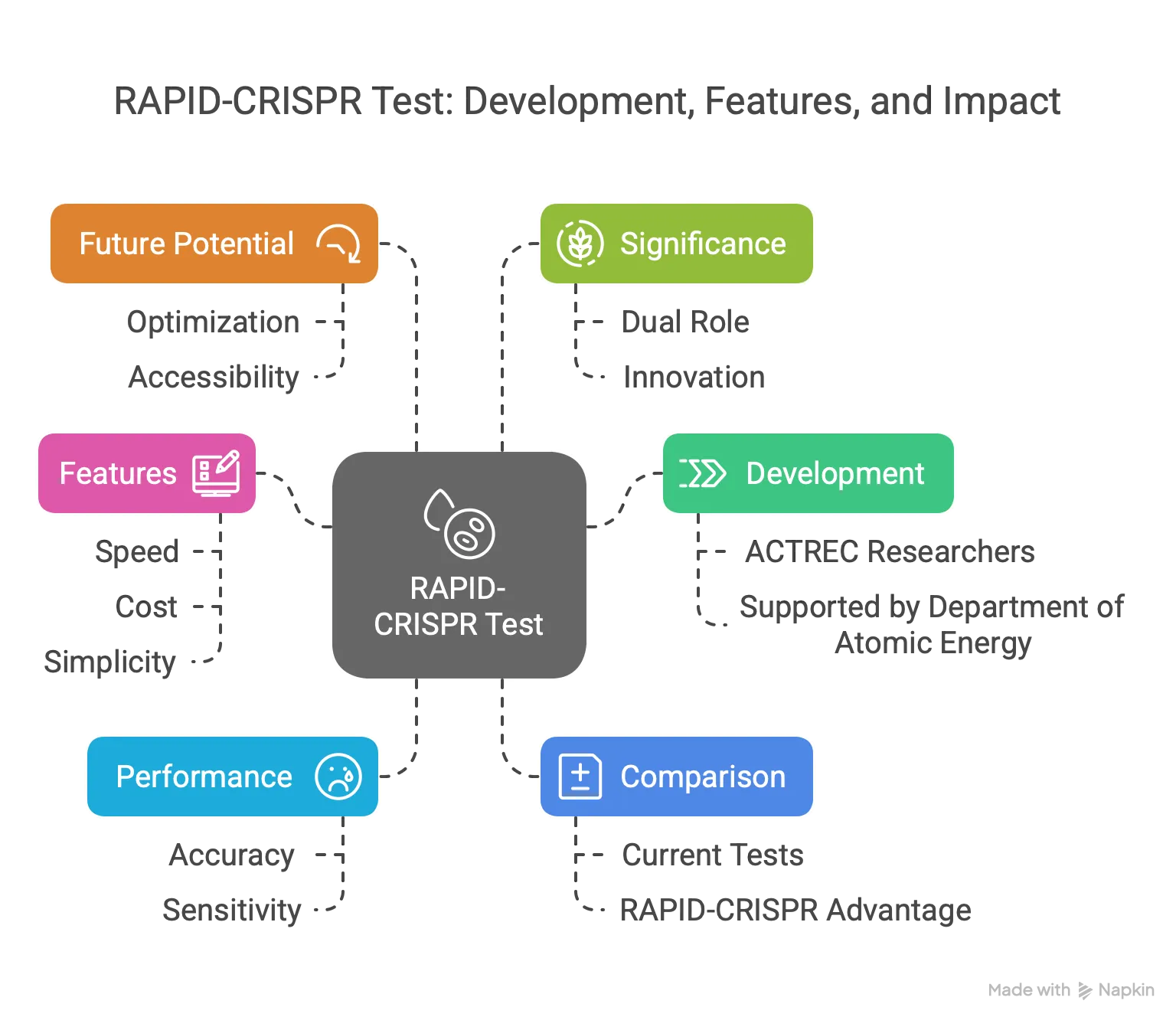
Key Points:
Overview of the Breakthrough
- Development: Researchers at the Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer (ACTREC), Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai, developed the RAPID-CRISPR test.
- Purpose: Detects acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), a rare and aggressive blood cancer.
- Publication: Study supported by the Department of Atomic Energy, published in Blood Advances.
Features of RAPID-CRISPR Test
- Speed: Delivers results in under three hours, much faster than conventional tests.
- Cost: More affordable than existing diagnostic methods.
- Simplicity: Does not require complex lab equipment, extensive setups, or highly trained personnel.
- Process: Uses a patient’s peripheral blood sample, with results displayed on a lateral flow strip (similar to a COVID-19 test).
- Detection: Identifies three isoforms (bcr1, bcr2, bcr3) of the PML-RARA gene mutation using three strips from a single sample.
Accuracy and Sensitivity
- Performance: Evaluated on 134 clinical samples, correctly identified APL in every case with no false positives or negatives.
- Sensitivity: Nearly 100% sensitivity and specificity; detects even a single copy of PML-RARA, making it 10 times more sensitive than the gold-standard RQ-PCR test.
Comparison with Existing Methods
- Current Tests: RQ-PCR requires specialized equipment to extract and amplify genetic material, increasing cost and complexity.
- RAPID-CRISPR Advantage: Works directly on patient samples, bypassing the need for advanced lab infrastructure.
Future Potential
- Optimization: Team aims to refine the test into a single-tube reaction detecting all isoforms with one strip.
- Accessibility: Designed to be a standard tool in hospitals worldwide, with potential for at-home testing after further development.
- Impact: Bridges diagnostic gaps, ensuring timely treatment for APL patients.
Significance of CRISPR Technology
- Dual Role: Beyond gene editing, CRISPR is leveraged for molecular diagnostics in this test.
- Innovation: RAPID stands for Redefined APL Identification, reflecting its diagnostic focus.
Contributors
- Team: Led by Professor Syed K. Hasan and PhD scholar Akash Maity at ACTREC.
Glossary
- CRISPR: Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats - A gene-editing and diagnostic tool derived from bacterial immune systems.
- RAPID-CRISPR: Redefined APL Identification CRISPR test - A fast, affordable diagnostic for acute promyelocytic leukemia.
- APL: Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia - A rare, aggressive blood cancer caused by PML-RARA gene mutation.
- PML-RARA: A genetic mutation driving APL, detectable by the RAPID-CRISPR test.
- RQ-PCR: Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction - The current gold-standard test for genetic detection, less sensitive than RAPID-CRISPR.
- Lateral Flow Strip: A simple diagnostic tool displaying results, akin to rapid antigen tests.
- ACTREC: Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer - A leading cancer research institute under Tata Memorial Centre.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/rare-blood-cancer-now-detectable-using-a-crispr-based-test/article69413020.ece