UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
Genetic Mapping of Indians: Unlocking Health and Heritage
Last Updated
13th April, 2025
Date Published
13th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

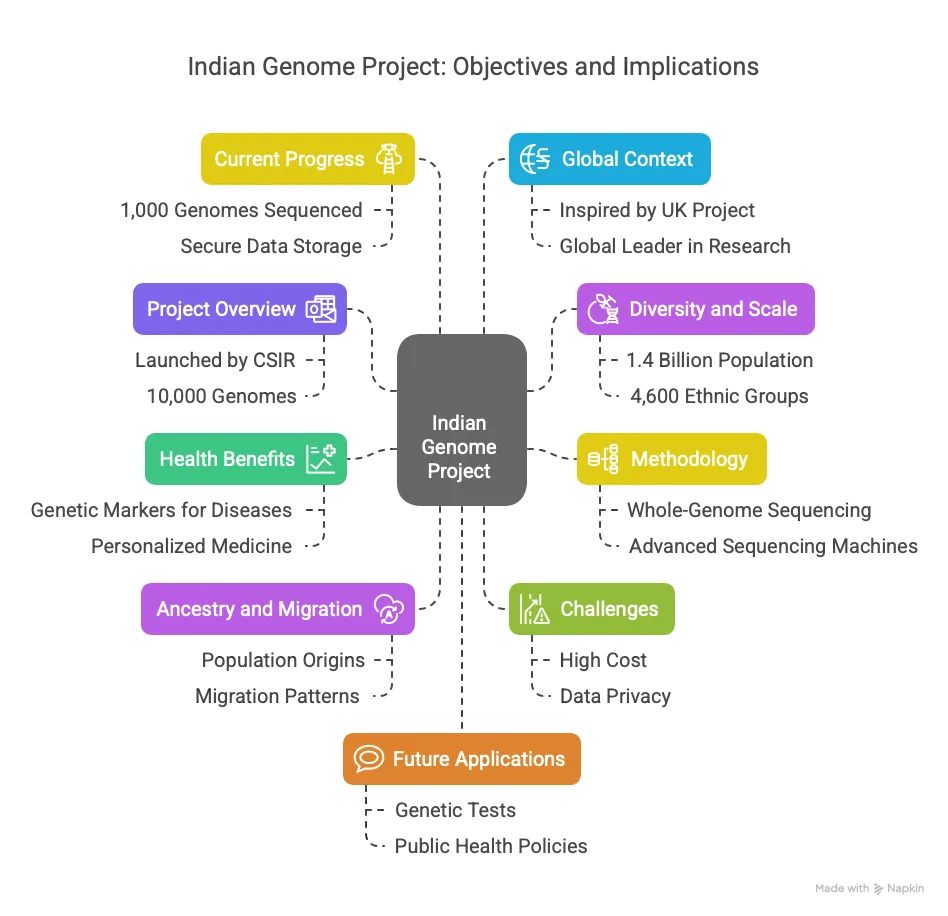
- Project Overview:
- Launched by CSIR’s Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) in Hyderabad.
- Seeks to sequence 10,000 Indian genomes to create a comprehensive genetic database.
- Diversity and Scale:
- India’s 1.4 billion population includes over 4,600 ethnic groups with distinct genetic profiles.
- Aims to capture variations across communities, addressing underrepresentation in global genomic data (only 0.1% of sequenced genomes are Indian).
- Methodology:
- Involves whole-genome sequencing to map all 3 billion base pairs in an individual’s DNA.
- Uses advanced sequencing machines and computational analysis at CCMB.
- Health Benefits:
- Identifies genetic markers for diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer, prevalent in India.
- Enables personalized medicine by tailoring treatments based on genetic profiles.
- Supports early diagnosis and prevention strategies for hereditary conditions.
- Ancestry and Migration:
- Traces population origins and migration patterns, revealing India’s historical diversity.
- Helps individuals understand their genetic heritage, similar to global platforms like 23andMe.
- Challenges:
- High cost of sequencing (₹50,000–₹1 lakh per genome) and need for advanced infrastructure.
- Requires collaboration with hospitals and research institutes for sample collection.
- Ethical concerns around data privacy and potential misuse of genetic information.
- Current Progress:
- CCMB has sequenced over 1,000 genomes, with plans to scale up through partnerships.
- Data stored securely with restricted access to protect privacy.
- Global Context:
- Inspired by projects like the UK’s 100,000 Genomes Project and Iceland’s deCODE initiative.
- Aims to position India as a leader in genomic research and precision medicine.
- Future Applications:
- Potential to develop India-specific genetic tests and therapies.
- May inform public health policies and targeted interventions for high-risk groups.
Key Terms:
- Genome: Complete set of DNA in an organism, containing all genetic information.
- Whole-genome sequencing: Process of determining the entire DNA sequence of an individual.
- Personalized medicine: Treatment tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup.
- Genetic markers: Specific DNA sequences linked to diseases or traits.
- CSIR: Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, India’s premier R&D organization.
- CCMB: Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, leading genomic research in India.
- Data privacy: Protection of sensitive genetic information from unauthorized access.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/how-will-genetic-mapping-of-indians-help-explained/article69443842.ece