Indian Express Concise
UPSC
Greenland's Independence & USA's Intervention In Greenland's Parliamentary Election and Its Implications.
Last Updated
12th March, 2025
Date Published
12th March, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

Election Overview:
- Greenland held a significant parliamentary election on March 11, 2025, with unofficial results expected shortly after.
- Approximately 40,000 of Greenland's 57,000 residents, primarily of Inuit heritage, voted to elect 31 members to the Inatsisartut (Parliament).
Key Issues at Stake:
Major local concerns include job creation, economic stability, and access to healthcare and education.
- The debate over independence from Denmark remains central, as Denmark still controls Greenland's defense and foreign policy.
- The ruling party, Inuit Ataqatigiit, advocates a cautious approach to independence, while the opposition party Naleraq pushes for quicker independence and closer ties with the US.
Greenland's Historical Context:
- Greenland was a Danish colony until it became an autonomous territory in 1953.
- The island relies heavily on Denmark for financial support, receiving around £480 million annually, which is crucial for its welfare programs.
US Interest in Greenland:
- The US has historically shown interest in Greenland due to its strategic location in the North Atlantic, which is vital for military and defense purposes.
- Greenland hosts the Pituffik Space Base, previously known as Thule Air Base, which is essential for monitoring threats from Russia, China, and North Korea.
- Trump's interest in purchasing Greenland is linked to its rare earth minerals, which are critical for technology and defence industries.
Public Sentiment and Environmental Concerns:
- Despite Trump's promises of economic benefits, about 85% of Greenlanders oppose becoming part of the US.
- Greenland prioritises environmental protection, having previously banned uranium mining, indicating a cautious approach to resource extraction.
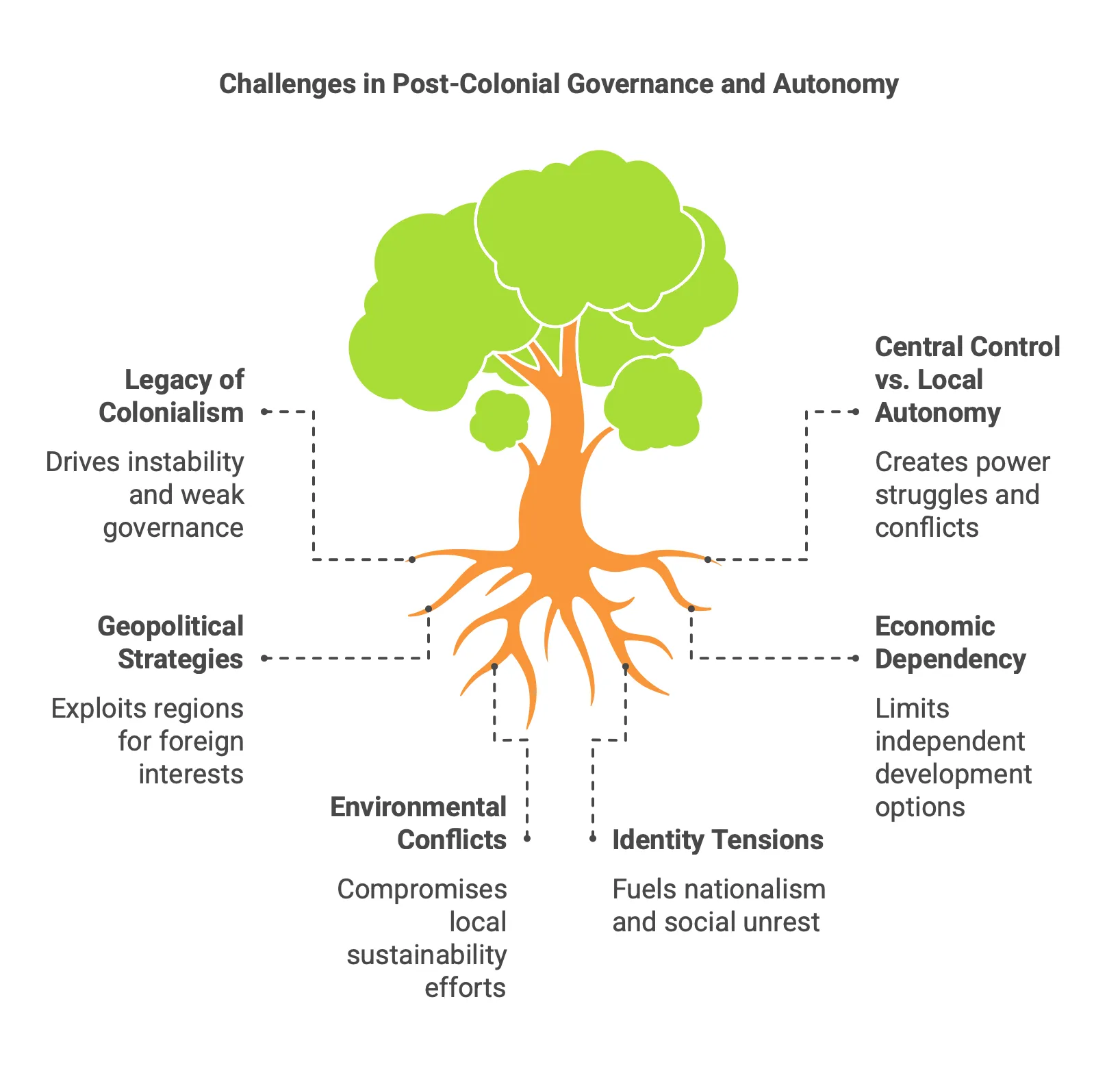
Complexities of Post-Colonial Governance, Local Autonomy, and International Interests
- Post-Colonial Governance:
- Legacy of Colonialism: Many post-colonial states grapple with the political, social, and economic legacies of colonial rule, including arbitrary borders, ethnic divisions, and centralised governance structures that may not reflect local realities.
- State-Building Challenges: Newly independent nations often face difficulties in establishing stable governance, leading to issues such as corruption, weak institutions, and lack of public trust.
- Identity and Nationalism: Post-colonial societies frequently navigate complex identities, balancing indigenous cultures and languages with the remnants of colonial influence, which can lead to tensions and conflicts.
- Local Autonomy:
- Decentralisation vs. Central Control: The push for local autonomy often conflicts with central government interests, leading to power struggles and demands for greater self-governance, as seen in regions like Greenland.
- Cultural and Political Representation: Local populations may seek representation and recognition of their rights, leading to movements for autonomy or independence, which can challenge national unity.
- Resource Management: Local communities often advocate for control over natural resources, leading to conflicts with national governments and international corporations, particularly in resource-rich regions.
- International Interests:
- Geopolitical Strategies: Post-colonial regions are often pawns in larger geopolitical strategies, with foreign powers seeking influence through economic aid, military presence, or resource extraction, as seen in the US interest in Greenland.
- Globalisation and Economic Dependency: Many post-colonial states remain economically dependent on former colonial powers or multinational corporations, complicating their ability to pursue independent development paths.
- Environmental Concerns: International interests in resource extraction can clash with local environmental priorities, leading to conflicts over sustainable development and the rights of indigenous populations.
- Interconnectedness of Themes:
- Human Rights and Self-Determination: The quest for local autonomy is often tied to broader human rights issues, including the right to self-determination, which is a significant theme in international law and relations.
- Balancing Act: Post-colonial governance requires balancing local autonomy with national interests and international pressures, often leading to complex negotiations and compromises.
- Impact on Policy Formulation: Understanding these complexities is crucial for civil servants, as they must navigate the interplay of local, national, and international factors in policy formulation and implementation.
Link To Original Article – https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/greenland-will-the-election-impact-trumps-plans-to-buy-9881108/