UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
Hadean Protocrust and Plate Tectonics: Key Insights from Macquarie Study
Last Updated
7th April, 2025
Date Published
7th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

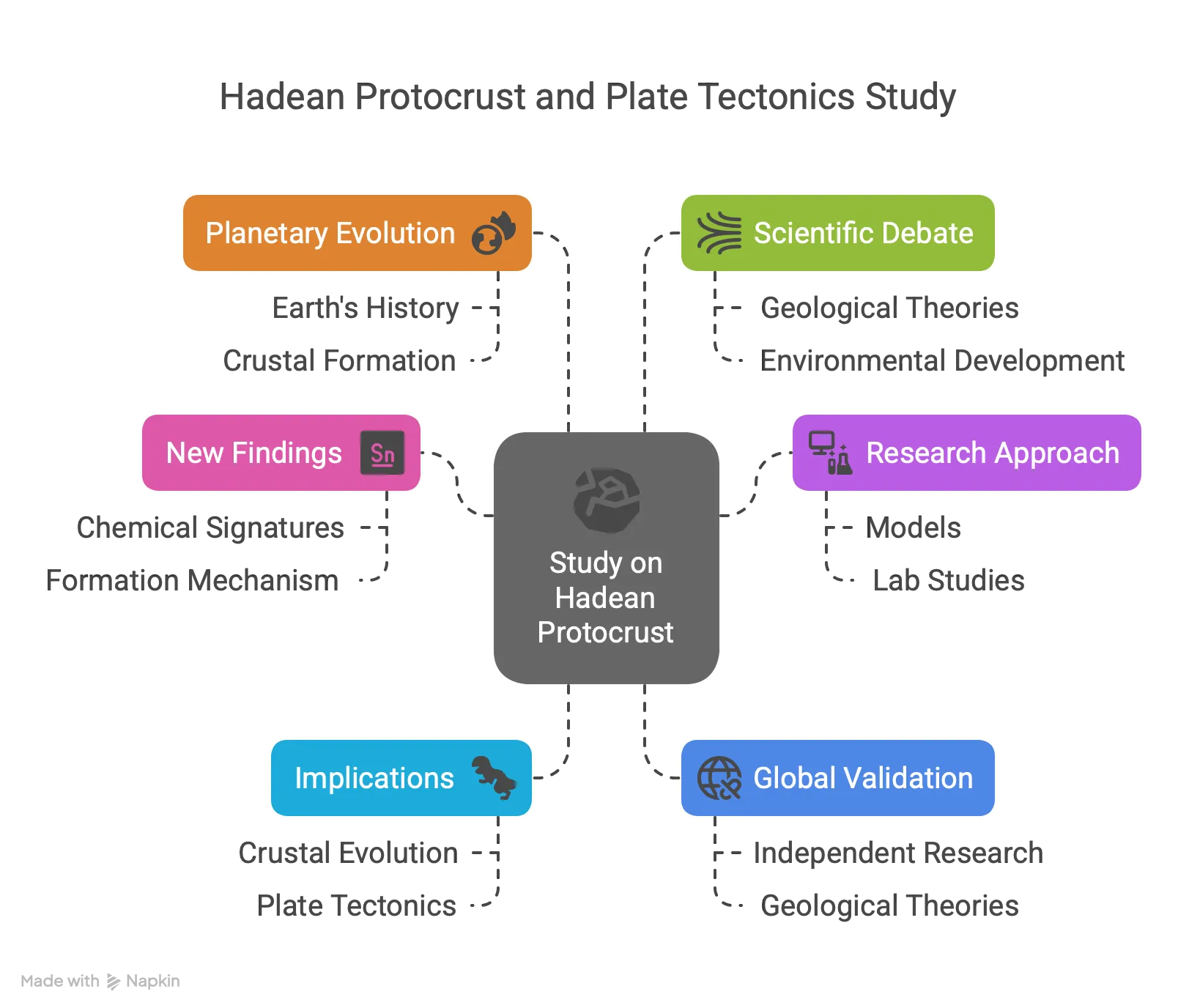
- Study Overview: A Macquarie University-led study challenges traditional views on the Hadean protocrust and the origin of plate tectonics, published on April 6, 2025.
- Hadean Protocrust Defined: The Hadean protocrust refers to Earth’s earliest crust formed 4.5-4 billion years ago, during the planet’s initial geologic eon marked by a molten surface and intense bombardment.
- New Finding: The study reveals that chemical signatures linked to plate tectonics existed in the Hadean protocrust, predating subduction processes, contradicting earlier geological assumptions.
- Research Approach: Using models and lab studies, researchers found that the protocrust bore traits similar to modern continental crust, questioning the necessity of subduction for these signatures.
- Implications for Plate Tectonics: This suggests plate tectonics may not have been the sole driver of early crustal evolution, prompting a rethink of when and how it began.
- Geological Timeline: Earth’s surface transitioned from a magma ocean to a solid crust within 200 million years, with continents forming as plates moved on the asthenospheric mantle.
- Chemical Signatures: Unique chemical markers in the crust, once attributed to subduction, were present in the protocrust, indicating a different formation mechanism.
- Global Validation Needed: The findings, while significant, require independent research to confirm their impact on established geological theories.
- Planetary Evolution: This discovery could reshape understanding of Earth’s early history and influence theories about crustal formation on other planets.
- Scientific Debate: The study fuels ongoing discussions about the timing and processes of plate tectonics, a critical aspect of Earth’s geological and environmental development.
Glossary
- Hadean Eon: Earth’s first geologic period (4.5-4 billion years ago), characterized by a molten surface and heavy meteor impacts.
- Protocrust: The initial, outermost solid layer of Earth formed as the magma ocean cooled.
- Plate Tectonics: The movement of Earth’s lithospheric plates, driving continental drift and geological activity.
- Subduction: The process where one tectonic plate slides beneath another, often linked to continental crust formation.
- Asthenospheric Mantle: A hot, semi-fluid layer beneath the crust, enabling plate movement.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/hadean-protocrust-plate-tectonics-macquarie-study-anomaly/article69416265.ece