UPSC
PIB
Indian Silk Industry: Weaving Tradition and Economic Growth
Last Updated
11th April, 2025
Date Published
11th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

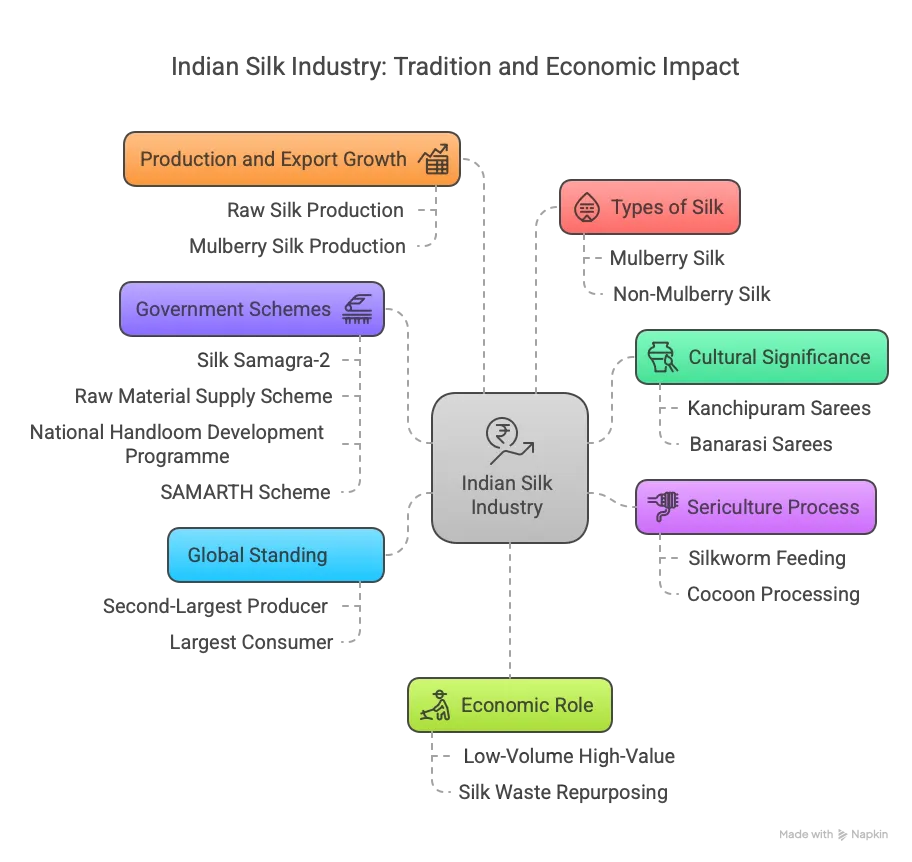
- Cultural Significance: Silk reflects India’s history and artistry, seen in Kanchipuram and Banarasi sarees, crafted by skilled artisans.
- Sericulture Process: Silkworms fed on mulberry, oak, castor, or arjun leaves spin cocoons, which are boiled, unraveled, and woven into silk fabric.
- Global Standing: India is the second-largest producer and largest consumer of silk globally.
- Production Growth:
- Raw silk: 31,906 MT (2017–18) to 38,913 MT (2023–24).
- Mulberry silk: 22,066 MT (2017–18) to 29,892 MT (2023–24).
- Mulberry plantations: 223,926 ha (2017–18) to 263,352 ha (2023–24).
- Export Growth: Silk and silk goods exports rose from ₹1,649.48 crore (2017–18) to ₹2,027.56 crore (2023–24); 3,348 MT of silk waste exported (2023–24).
- Types of Silk:
- Mulberry Silk: 92% of production; soft, shiny, used for luxury sarees; produced in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Jammu & Kashmir, West Bengal.
- Non-Mulberry (Vanya) Silk: Earthy, durable, eco-friendly; from Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, northeastern states.
- Economic Role: Low-volume, high-value product (0.2% of global textiles); supports rural employment and foreign exchange earnings.
- Silk Waste: Imperfect fibers repurposed for yarn, fabric, or recycled products.
- Government Schemes:
- Silk Samagra-2 (2021–2026): ₹4,679.85 crore budget; components include R&D, seed organizations, market development, and quality certification.
- Central assistance: ₹1,075.58 crore, benefiting 78,000+ people.
- Funding: Andhra Pradesh (₹72.50 crore), Telangana (₹40.66 crore).
- Raw Material Supply Scheme (RMSS): Supplies 340 lakh kg of subsidized yarn (2023–24) for handloom weavers.
- National Handloom Development Programme (NHDP): Supports weavers with raw materials, design, technology, and marketing; builds infrastructure like Urban Haats.
- SAMARTH Scheme: ₹495 crore (2024–2026) to train 3 lakh people in textiles, including silk, focusing on entry-level and upskilling.
- Impact: Schemes enhance silk quality, quantity, and rural livelihoods, preserving cultural traditions.
Glossary:
- Sericulture: Rearing silkworms to produce silk through cocoon processing.
- Mulberry Silk: Shiny silk from silkworms fed exclusively on mulberry leaves.
- Non-Mulberry Silk: Durable silk from wild silkworms feeding on oak, castor, or arjun leaves.
- Silk Waste: Leftover fibers from silk production repurposed for lower-quality products.
- Silk Samagra: Central scheme to boost silk production, quality, and market development.