UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
Indian Stock Market Crash: Key Drivers of the April 7, 2025, Downturn
Last Updated
7th April, 2025
Date Published
7th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

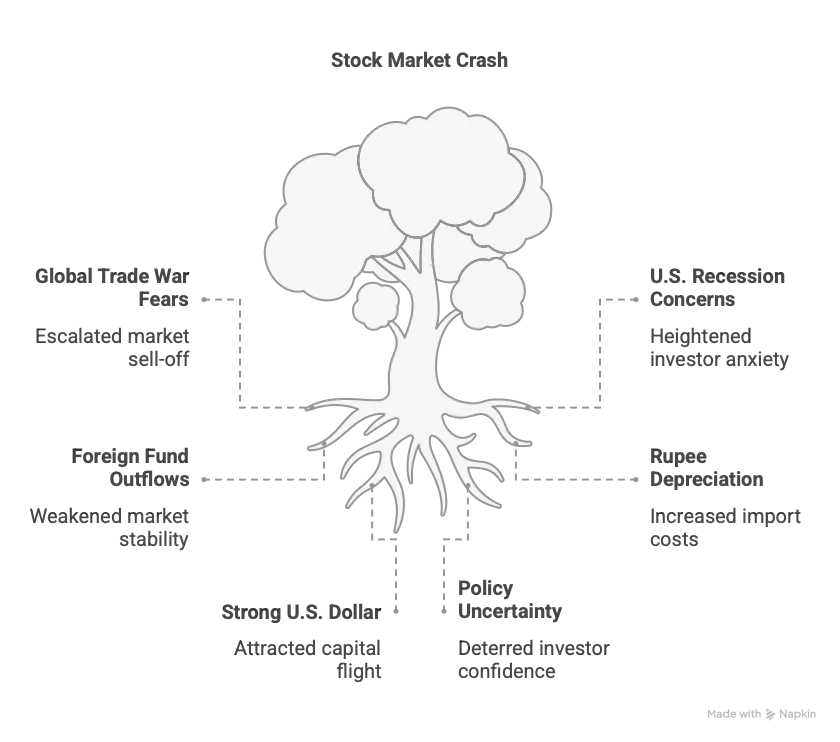
- Global Trade War Fears: Escalating U.S.-China trade tensions, triggered by U.S. tariffs announced on April 2, 2025, led to a global market sell-off, impacting Indian shares.
- U.S. Recession Concerns: Weak U.S. economic indicators, including disappointing job data, heightened recession fears, causing a ripple effect on Indian markets.
- Foreign Fund Outflows: Foreign institutional investors withdrew significant capital, with outflows exceeding ₹61,000 crore in 2025, weakening market stability.
- Rupee Depreciation: The Indian rupee fell to 85.70–85.75 per U.S. dollar on April 3, 2025, raising import costs and investor concerns.
- Strong U.S. Dollar: A rising U.S. dollar index, nearing 107.35, made emerging markets like India less attractive, prompting capital flight.
- Sectoral Declines: All 13 major sectors slumped, with small-caps and mid-caps losing 10% and 7.3%, respectively, reflecting broad-based panic.
- Commodity Price Volatility: Falling oil prices and commodities, linked to global slowdown fears, eroded investor confidence in export-reliant sectors.
- Policy Uncertainty: Uncertainty around the Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy decision, due April 9, 2025, added pressure on market sentiment.
- Global Market Sync: Sharp declines in Wall Street (S&P 500 down 3.3%) and Asian markets (Nikkei 225 down 6.5%) amplified the domestic crash.
- High Market Valuations: Overvalued stocks, following a 2024 rally, faced a correction as trade and economic risks surfaced.
Glossary
- Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs): Overseas entities investing in Indian financial markets, influencing liquidity.
- Nifty 50: A benchmark index of the National Stock Exchange, tracking 50 major Indian companies.
- BSE Sensex: The Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitive Index, representing 30 key stocks.
- Capital Flight: Rapid withdrawal of investment capital from a country due to economic or political instability.
- Monetary Policy: Central bank actions (e.g., by RBI) to regulate money supply and interest rates.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/business/markets/indian-stock-market-crash-live-april-7-2025/article69421854.ece