UPSC
PIB
India’s Coal Sector: Milestones and Future Prospects
Last Updated
5th April, 2025
Date Published
5th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

India’s coal industry plays a pivotal role in the nation’s energy security, economic growth, and industrial development. Achieving a historic milestone of over one billion tonnes in coal production in FY 2024-25, the sector reflects a blend of growth, sustainability efforts, and technological advancements. This summary highlights key achievements, government initiatives, and challenges, offering a comprehensive overview for aspirants preparing for competitive examinations.
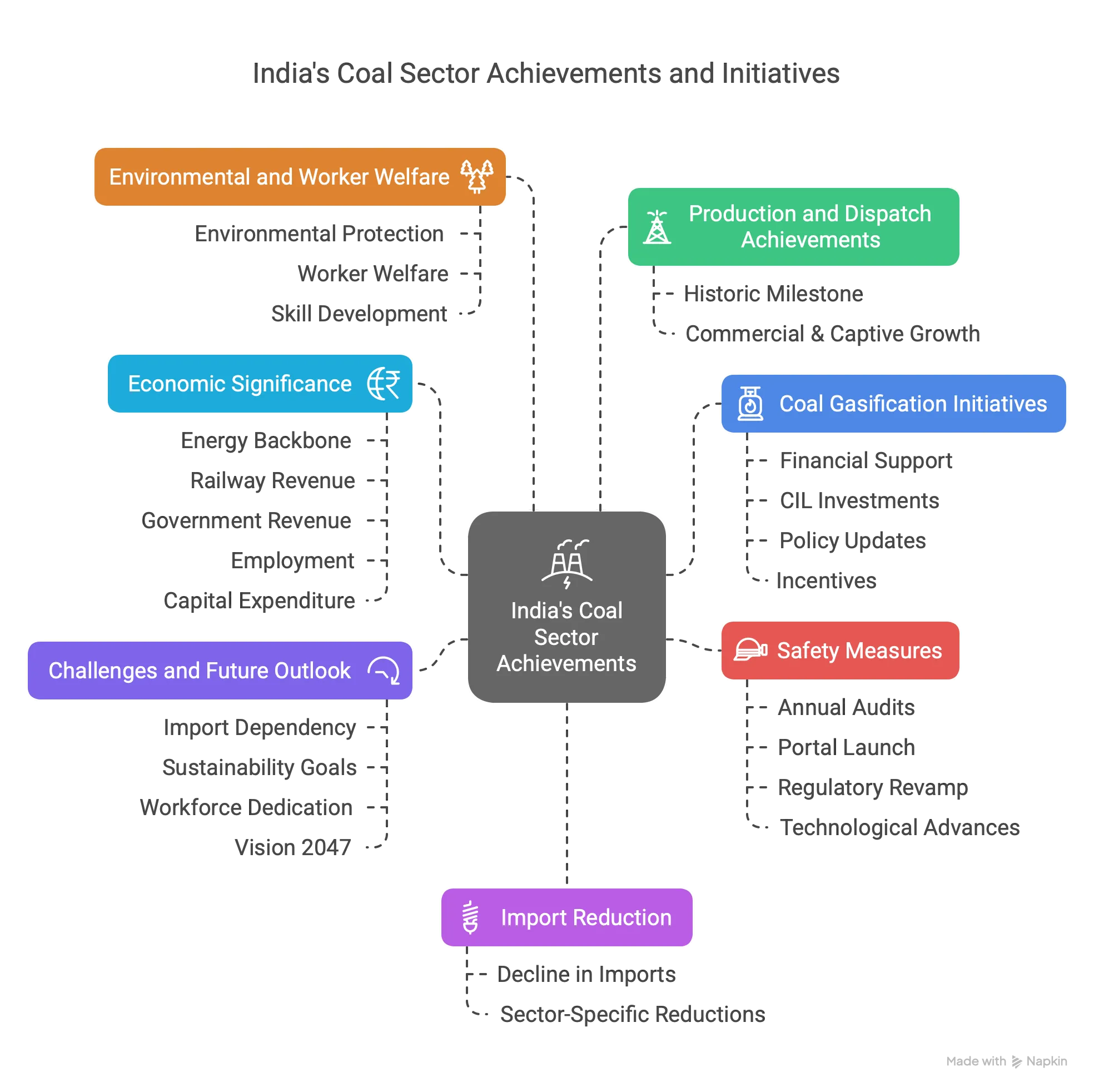
Key Points:
Production and Dispatch Achievements:
- Historic Milestone: India surpassed 1 billion tonnes (BT) of coal production on March 20, 2025, in FY 2024-25, reaching 1047.57 million tonnes (MT) (provisional), a 4.99% increase from 997.83 MT in FY 2023-24.
- Commercial & Captive Growth: Production from commercial, captive, and other entities rose to 197.50 MT (provisional), up 28.11% from 154.16 MT the previous year.
- Dispatch Milestone: Coal dispatch crossed 1 BT, reaching 1024.99 MT (provisional) in FY 2024-25, a 5.34% rise from 973.01 MT in FY 2023-24.
- Dispatch Surge: Dispatch from commercial, captive, and other entities increased by 31.39%, reaching 196.83 MT (provisional) from 149.81 MT.
Import Reduction:
- Decline in Imports: Coal imports dropped 8.4% to 183.42 MT in April-December 2024 from 200.19 MT in the same period of FY 2023-24, saving $5.43 billion (₹42,315.7 crore) in foreign exchange.
- Sector-Specific Reductions: Non-Regulated Sector imports fell by 12.01%, and imports for blending in thermal power plants decreased by 29.8%, despite a 3.53% rise in coal-based power generation.
- Government Push: Initiatives like Commercial Coal Mining and Mission Coking Coal increased domestic output by 6.11%, reducing import dependency.
Economic Significance:
- Energy Backbone: Coal powers over 74% of India’s electricity and contributes 55% to the national energy mix, with a projected share of 55% by 2030 and 27% by 2047.
- Railway Revenue: Coal accounts for 49% of railway freight income, generating ₹82,275 crore in FY 2022-23, over 33% of total railway earnings.
- Government Revenue: The sector contributes over ₹70,000 crore annually via royalties, GST, and levies, with ₹23,184.86 crore in royalties in FY 2022-23.
- Employment: Provides jobs to over 239,000 workers in Coal India Ltd, plus thousands in contractual and transport roles.
- Capital Expenditure: Annual average investment of ₹18,255 crore over the past five years for infrastructure and resource optimization.
Coal Gasification Initiatives:
- Financial Support: ₹8,500 crore approved on January 24, 2024, for coal/lignite gasification projects for PSUs and private players.
- CIL Investments: Coal India Ltd (CIL) to collaborate with BHEL and GAIL for gasification projects.
- Policy Updates: “Production of Syngas” added as a sub-sector in 2022 under NRS linkage auctions with regulated pricing for seven years.
- Incentives: 50% revenue share rebate for coal used in gasification in commercial coal block auctions (minimum 10% coal usage).
- Applications: Gasification produces syngas for methanol, fertilizers, ammonium nitrate, and synthetic natural gas (SNG), aiding sustainability.
Safety Measures:
- Annual Audits: Safety audits mandated under the “Safety Health Management System Audit” guidelines (December 2023).
- Portal Launch: “National Coal Mine Safety Report Portal” launched on December 17, 2024, with a safety audit module.
- Regulatory Revamp: Coal Mines Regulations 1957 updated to 2017, focusing on modernization, mechanization, and emergency response.
- Technological Advances:
- Blast-free mining (Continuous Miner, Surface Miner, etc.).
- Real-time monitoring via Environmental Telemonitoring System (ETMS) and Gas Chromatographs.
- Strata control with mechanized roof bolting and advanced instrumentation.
- Dust control via Fog Cannons and sprinkler systems.
- Simulator-based and VR training for Heavy Earth Moving Machinery (HEMM) operators.
- Slope stability monitoring using Total Stations, 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanning, and GPS-based systems.
Environmental and Worker Welfare:
- Environmental Protection: Mandatory Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) studies and ongoing monitoring.
- Worker Welfare: Mines Rules, 1955, ensure health checks, first aid, shelters, canteens, housing, water, scholarships, healthcare, and compassionate employment.
- Skill Development: Vocational training, simulator-based programs, and workshops on drilling, blasting, and fire safety.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
- Import Dependency: Shortages in coking and high-grade thermal coal necessitate continued imports.
- Sustainability Goals: Coal gasification and safety advancements align with long-term environmental sustainability and energy security.
- Workforce Dedication: 5 lakh mine workers across 350+ coal mines instrumental in achieving milestones.
- Vision 2047: Coal sector to remain a cornerstone of India’s self-reliance and development by 2047.
Glossary
- Coal Gasification: Process of converting coal into syngas for producing chemicals and fuels.
- Syngas: Synthetic gas mixture used for methanol, fertilizers, and SNG production.
- Commercial Coal Mining: Policy allowing private sector participation in coal extraction.
- Mission Coking Coal: Initiative to boost domestic coking coal production.
- Dispatch: Transportation and distribution of coal to consumers.
- Energy Mix: Proportion of various energy sources in total energy supply.
- Royalty: Payment made to governments for resource extraction.
- Strata Control: Techniques to manage underground rock stability in mines.
- EIA: Environmental Impact Assessment to evaluate project environmental effects.
- HEMM: Heavy Earth Moving Machinery used in mining operations.