UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
Iran’s Nuclear Programme: A Global Concern
Last Updated
13th April, 2025
Date Published
13th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

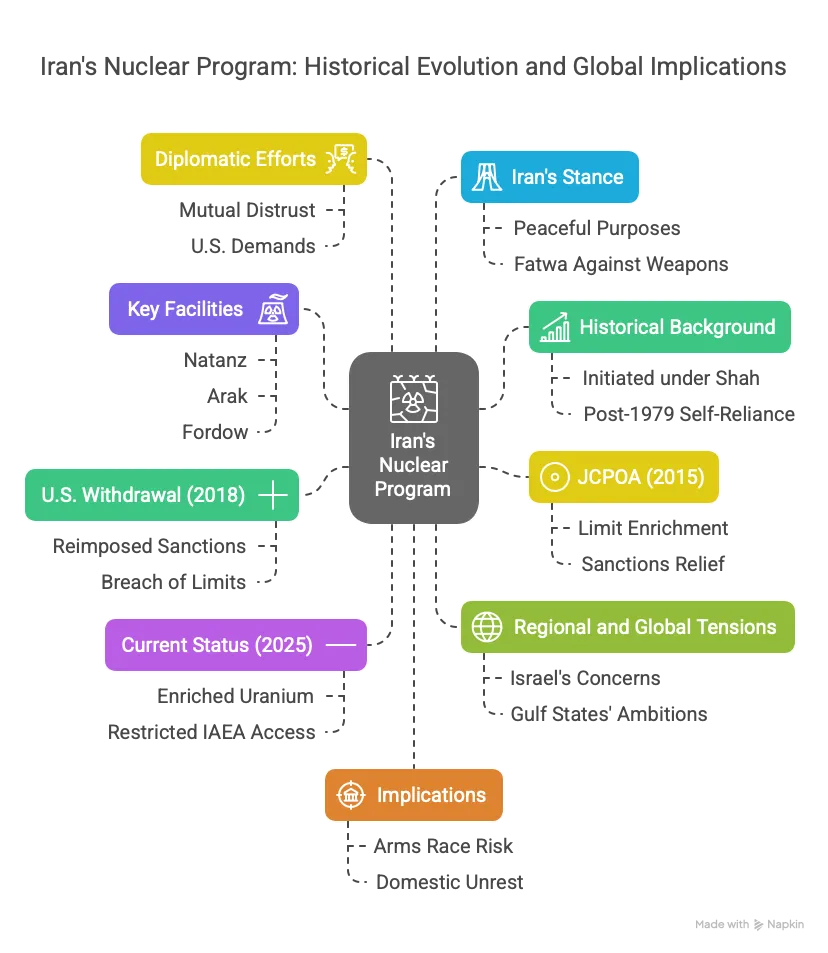
- Historical Background:
- Initiated in the 1950s under the Shah with U.S. support for civilian nuclear energy.
- Post-1979 Islamic Revolution, Iran pursued self-reliance in nuclear technology amid Western suspicion of weaponization.
- Key Facilities:
- Natanz: Major uranium enrichment site with advanced centrifuges.
- Arak: Heavy-water reactor, capable of producing plutonium (redesigned under JCPOA).
- Fordow: Underground enrichment facility, less accessible to monitoring.
- JCPOA (2015):
- Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action signed by Iran, P5+1 (U.S., UK, France, Russia, China, Germany), and EU.
- Iran agreed to limit uranium enrichment to 3.67%, reduce centrifuge numbers, and allow IAEA inspections in exchange for sanctions relief.
- U.S. Withdrawal (2018):
- President Trump exited the JCPOA, reimposing sanctions, citing Iran’s regional activities and missile programme.
- Iran gradually breached JCPOA limits, enriching uranium to 60% (near weapons-grade 90%).
- Current Status (2025):
- Iran possesses enough enriched uranium for multiple nuclear weapons if further processed, per IAEA reports.
- Advanced centrifuges (IR-6, IR-9) enhance enrichment speed, raising concerns.
- IAEA access restricted since 2021, complicating verification.
- Regional and Global Tensions:
- Israel views Iran’s programme as an existential threat, conducting covert operations (e.g., Stuxnet, scientist assassinations).
- Gulf states, led by Saudi Arabia, seek U.S. security guarantees and consider their own nuclear ambitions.
- Russia and China maintain economic ties with Iran, complicating Western sanctions.
- Diplomatic Efforts:
- Post-2020, talks to revive JCPOA stalled over mutual distrust and U.S. demands on non-nuclear issues.
- Iran insists on sanctions relief and guarantees against future U.S. withdrawal.
- Iran’s Stance:
- Claims nuclear programme is for peaceful purposes (energy, medical isotopes).
- Supreme Leader Khamenei issued a fatwa against nuclear weapons, though skepticism persists.
- Implications:
- Risk of regional arms race if Iran advances toward nuclear capability.
- Sanctions have crippled Iran’s economy, fueling domestic unrest.
- Failure of diplomacy could lead to military escalation, involving U.S. and Israel.
Key Terms:
- JCPOA: 2015 nuclear deal limiting Iran’s nuclear activities for sanctions relief.
- Uranium enrichment: Process to increase uranium-235 concentration for reactors or weapons.
- IAEA: International Atomic Energy Agency, monitors nuclear compliance.
- Centrifuges: Machines used to enrich uranium by separating isotopes.
- Sanctions: Economic penalties to pressure Iran’s nuclear compliance.
- P5+1: Group of six powers negotiating with Iran (U.S., UK, France, Russia, China, Germany).
- Nuclear weaponization: Development of nuclear material into functional weapons.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/irans-nuclear-programme-an-atomic-tug-of-war/article69443845.ece