UPSC
Exam Nugget
Jyotiba Phule: Pioneer of Social Reform in India
Last Updated
11th April, 2025
Date Published
11th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

- Background: Born on April 11, 1827, into the Mali caste, traditionally gardeners and florists, in Maharashtra.
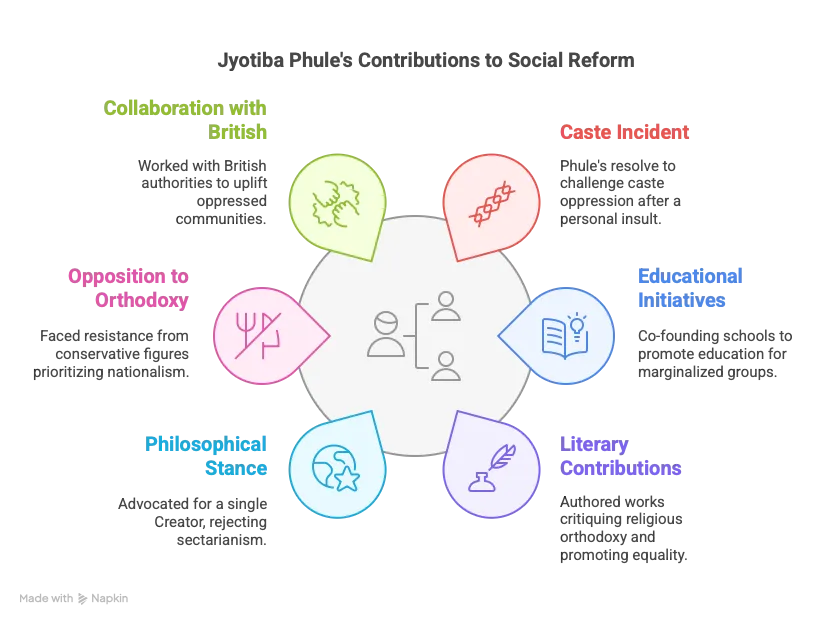
- Caste Incident: In 1848, insulted at a Brahmin friend’s wedding due to his caste, prompting his resolve to challenge caste oppression.
- Educational Influence: Visited a girls’ school in Ahmednagar run by missionary Cynthia Farrar and was inspired by Thomas Paine’s Age of Reason, critiquing religious orthodoxy.
- Educational Initiatives: In 1848, at age 21, co-founded India’s first girls’ school with wife Savitribai; opened 18 more schools within three years.
- Night Schools: By 1855, established night schools in Pune for workers, farmers, and working women to access education despite daytime commitments.
- Satyashodhak Samaj: Founded the Society of Truth-Seekers in September 1873 to promote equality and counter upper-caste-dominated reform movements like Brahmo Samaj, Prarthana Samaj, and Arya Samaj.
- Literary Contributions: Authored Sarvajanik Satya Dharma Pustak, critiquing religious texts for lacking universal truth and promoting sectarianism due to interpolations.
- Philosophical Stance: Advocated a single Creator for the universe, rejecting sectarianism and supremacism in religious practices.
- Opposition to Orthodoxy: Faced resistance from conservative figures like Vishnu Shashtri Chiplunkar and Bal Gangadhar Tilak, who prioritized nationalist agendas.
- Collaboration with British: Worked with the British government to uplift untouchables, depressed castes, and women, viewing them as allies against caste oppression.
- Humanitarian Act: Bailed out Tilak and Gopal Ganesh Agarkar from Mumbai’s Dongri Jail, despite ideological differences.
- View on 1857 Revolt: Did not support the Sepoy Revolt, seeing it as a potential return to Peshwa theocracy, which he believed would harm Dalits.
- Critique of Caste System: In Gulamgiri (Slavery), compared Brahminical caste oppression to American slavery, condemning its dehumanizing impact.
- Legacy: Recognized as a key figure in social reform, influencing movements for equality, education, and emancipation of marginalized groups.
Glossary:
- Mali Caste: A traditional gardening and florist community in Maharashtra.
- Caste Oppression: Discrimination and exclusion based on hierarchical social divisions.
- Satyashodhak Samaj: A society founded in 1873 to promote truth-seeking and equality across castes.
- Sectarianism: Division and conflict arising from rigid religious or social group affiliations.
- Gulamgiri: A book by Phule critiquing caste-based slavery and social inequalities.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/books/phule-a-constant-gardener-of-social-revolution/article69435103.ece