UPSC
Exam Nugget
Katchatheevu Island: A Key to India-Sri Lanka Relations
Last Updated
7th April, 2025
Date Published
7th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

- Location and Context: Katchatheevu is a small, uninhabited island in the Palk Strait, between Tamil Nadu, India, and northern Sri Lanka, covering 285 acres.
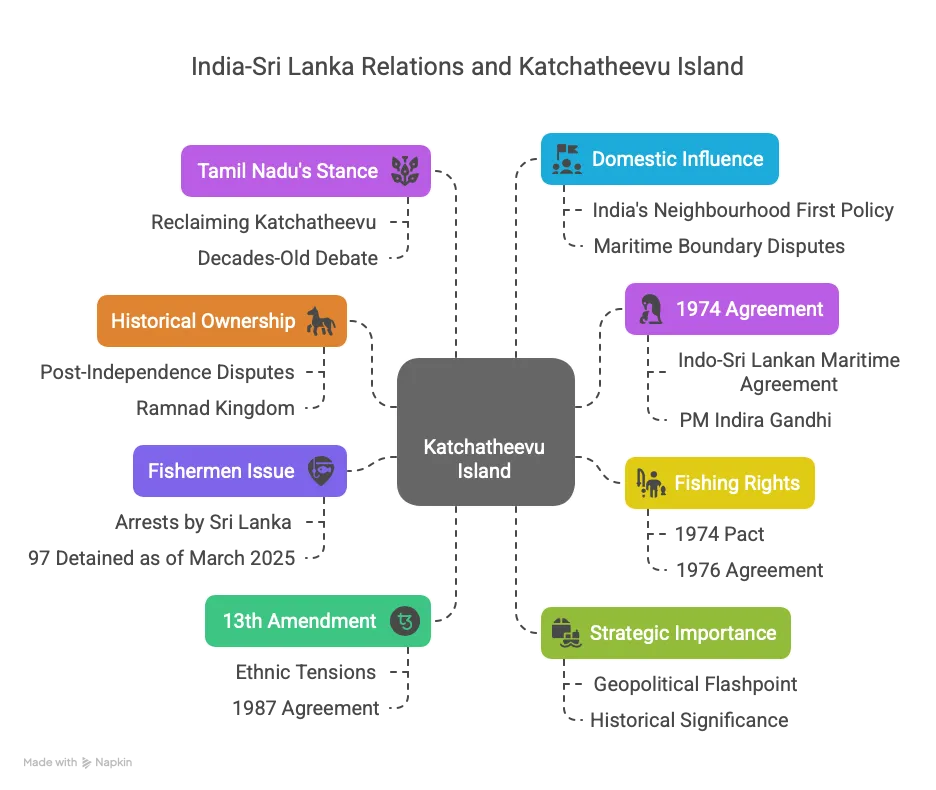
- Historical Ownership: It was part of the Ramnad Kingdom in Tamil Nadu until British rule, with ownership disputes persisting post-independence in 1947-48.
- 1974 Agreement: India ceded Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka via the Indo-Sri Lankan Maritime Agreement, signed on June 26 in Colombo and June 28 in New Delhi, under PM Indira Gandhi.
- Fishing Rights: The 1974 pact allowed Indian fishermen access to the island, but a 1976 agreement relinquished these rights, restricting them to Indian waters.
- Fishermen Issue: Tamil Nadu fishermen face arrests by Sri Lanka for crossing the maritime boundary, with 97 detained as of March 2025, averaging two arrests daily.
- 13th Amendment Link: India pushes for Sri Lanka’s 13th Amendment (1987), promising Tamil autonomy, as a solution to ethnic tensions tied to the Katchatheevu dispute.
- Strategic Importance: The island’s location near shipping lanes and its historical significance make it a geopolitical flashpoint in India-Sri Lanka ties.
- Tamil Nadu’s Stance: In April 2025, CM M.K. Stalin urged the Centre to reclaim Katchatheevu to protect fishermen’s rights, reviving a decades-old debate.
- Domestic Influence: Tamil Nadu’s concerns over fishermen’s livelihoods shape India’s foreign policy, balancing regional sentiment with bilateral relations.
- Current Relevance: The issue tests India’s “Neighbourhood First” policy, highlighting maritime boundary disputes and humanitarian concerns in bilateral diplomacy.
Glossary
- Palk Strait: Narrow waterway separating Tamil Nadu, India, from Sri Lanka.
- Indo-Sri Lankan Maritime Agreement: 1974 pact defining maritime boundaries, ceding Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka.
- 13th Amendment: 1987 Sri Lankan constitutional change for Tamil devolution, backed by India.
- Ramnad Kingdom: Historical Tamil Nadu princely state claiming Katchatheevu pre-independence.
- Neighbourhood First Policy: India’s diplomatic focus on fostering ties with neighboring countries.
Link To The Original Article – https://indianexpress.com/article/upsc-current-affairs/upsc-essentials/knowledge-nuggetkatchatheevu-island-upsc-india-sri-lanka-9924631/