UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
RBI Monetary Policy 2025 – MPC cuts repo rate by 25 basis points
Last Updated
9th April, 2025
Date Published
9th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

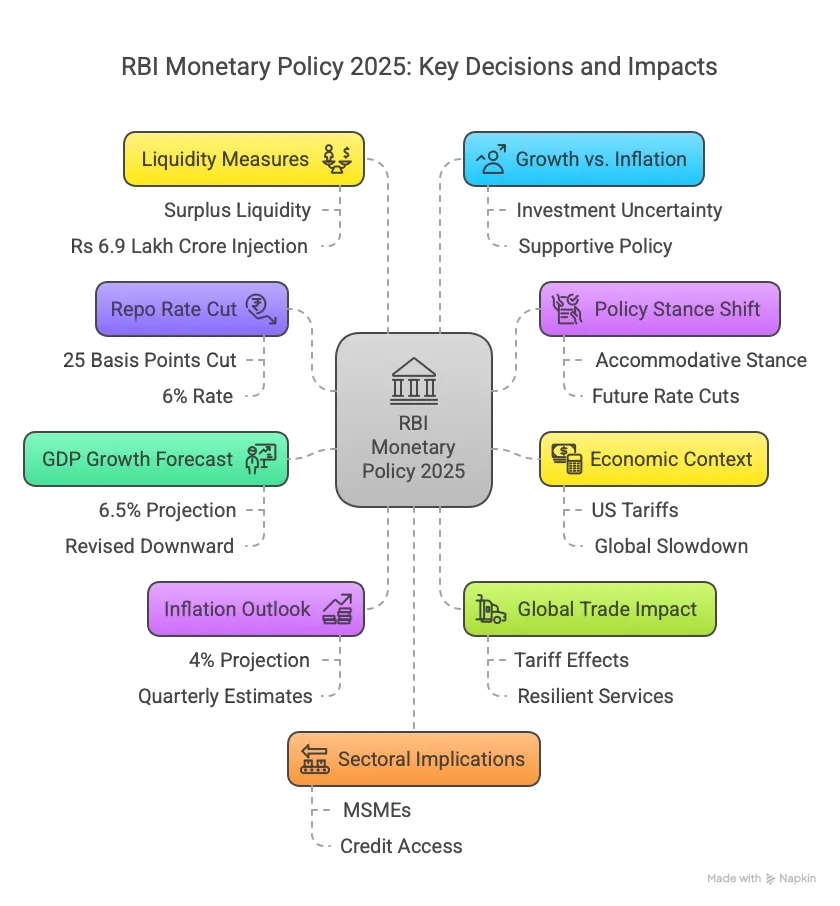
- Repo Rate Cut: On April 9, 2025, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reduced the repo rate by 25 basis points to 6%, marking the second consecutive cut after February 2025.
- Policy Stance Shift: The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) changed its stance from "neutral" to "accommodative," signaling potential future rate cuts to boost economic growth.
- Economic Context: The decision was influenced by global trade uncertainties, particularly US tariffs under President Donald Trump, posing risks to India’s growth and exports.
- GDP Growth Forecast: RBI revised the GDP growth projection for 2025-26 to 6.5% (down from 6.7%), reflecting concerns over global economic slowdown.
- Inflation Outlook: Inflation for 2025-26 is projected at 4%, with quarterly estimates ranging from 3.6% to 4.4%, assuming a normal monsoon.
- Global Trade Impact: Governor Sanjay Malhotra highlighted that tariff-related measures could dampen merchandise exports, though services exports remain resilient.
- Liquidity Measures: System liquidity moved from a deficit in January 2025 to a surplus by March, aided by RBI’s injection of Rs 6.9 lakh crore.
- Growth vs. Inflation: Malhotra emphasized that uncertainty affects investment and spending, necessitating a supportive monetary policy to stimulate the economy.
- Sectoral Implications: Lower borrowing costs are expected to benefit MSMEs, contributing 30% to GDP and 40% to exports, by easing credit access.
- Future Policy Hint: The accommodative stance suggests a possible rate cut in June 2025, absent major economic shocks, to sustain growth momentum.
Glossary
- Repo Rate: The rate at which RBI lends to commercial banks, influencing overall interest rates in the economy.
- Monetary Policy Committee (MPC): A six-member body, chaired by the RBI Governor, responsible for setting interest rates.
- Accommodative Stance: A policy approach favoring lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and economic activity.
- GDP Growth: The annual percentage increase in the value of goods and services produced in an economy.
- Inflation: The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power.
- Liquidity: The availability of liquid assets (cash) in the financial system to facilitate transactions.
- MSMEs: Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, key drivers of employment and economic output in India.
- Tariffs: Taxes imposed on imported goods, affecting trade and economic growth.
- Basis Points (bps): One hundredth of a percentage point (e.g., 25 bps = 0.25%).
- RBI Governor: The head of the Reserve Bank of India, currently Sanjay Malhotra, appointed in December 2024.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/rbi-monetary-policy-rates-governor-sanjay-malhotra-april-9-2025/article69429776.ece