UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
South Korea’s Political Crisis: Lessons in Democracy and Governance
Last Updated
10th April, 2025
Date Published
10th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

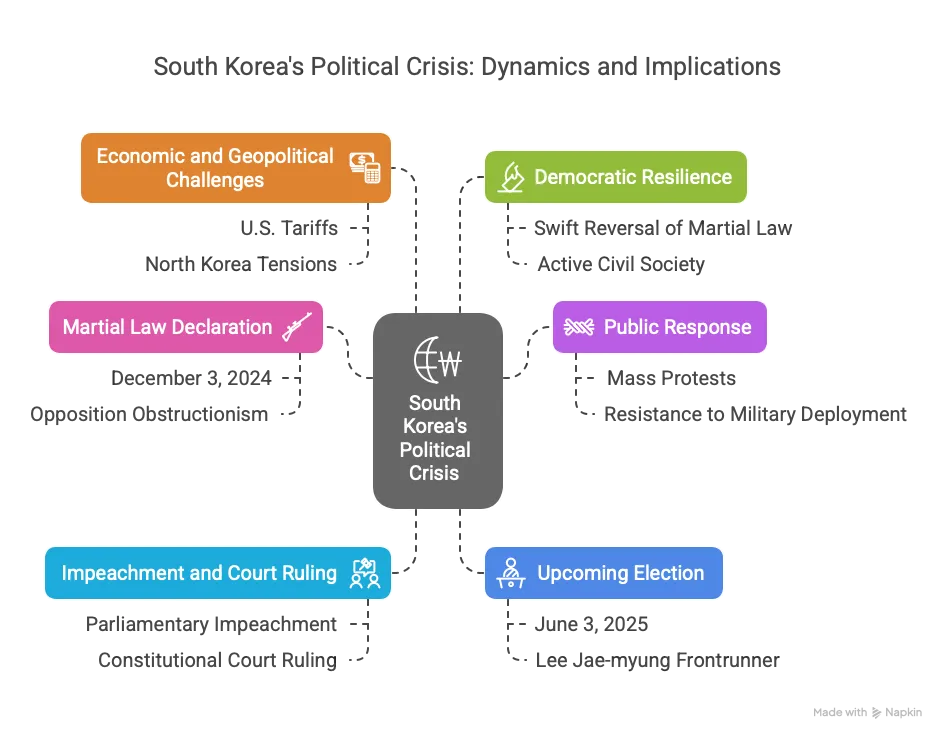
- Martial Law Trigger: On December 3, 2024, President Yoon Suk Yeol declared martial law, citing opposition obstructionism and alleged "anti-state" forces, plunging South Korea into political turmoil.
- Public Backlash: The move sparked massive protests, with citizens and opposition lawmakers resisting military deployment at the National Assembly, reflecting deep democratic resilience.
- Impeachment Process: Parliament impeached Yoon on December 14, 2024, with a second vote succeeding on December 27, suspending his powers and transferring them to Prime Minister Han Duck-soo.
- Court Ruling: On April 4, 2025, the Constitutional Court unanimously upheld Yoon’s impeachment, removing him from office for violating constitutional norms and public trust.
- Election Ahead: A snap presidential election is scheduled for June 3, 2025, with opposition leader Lee Jae-myung of the Democratic Party emerging as a frontrunner after his party’s parliamentary success.
- Economic Challenges: The crisis coincides with external pressures, including U.S. tariffs of 25% on South Korean exports, testing the next leader’s economic management skills.
- Polarization Exposed: Yoon’s actions deepened societal divides between conservatives (pro-Yoon) and progressives, highlighting the fragility of political consensus in a democracy.
- Democratic Triumph: The swift reversal of martial law within hours and Yoon’s removal underscore South Korea’s robust democratic institutions and active civil society.
- Global Context: The turmoil reflects broader challenges of governance under economic strain and geopolitical tensions, notably with North Korea and U.S. relations.
- Leadership Test: The incoming president must heal divisions, restore trust in institutions, and address both domestic stability and international trade dynamics.
Glossary
- Martial Law: Temporary military rule suspending civilian governance, invoked by Yoon to assert control.
- Impeachment: Legislative process to remove a leader, successfully applied to Yoon by South Korea’s parliament.
- National Assembly: South Korea’s unicameral legislature, central to the crisis and democratic response.
- Constitutional Court: Judicial body that upheld Yoon’s removal, ensuring constitutional adherence.
- Democratic Party: Main opposition party, led by Lee Jae-myung, poised to influence the upcoming election.
Link To The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/what-is-the-current-political-situation-in-south-korea-explained/article69428413.ece