UPSC
The Hindu Briefs
Wildfires and Climate Change: The Arctic Boreal Zone’s Carbon Crisis
Last Updated
10th April, 2025
Date Published
10th April, 2025
Share This Post With Someone

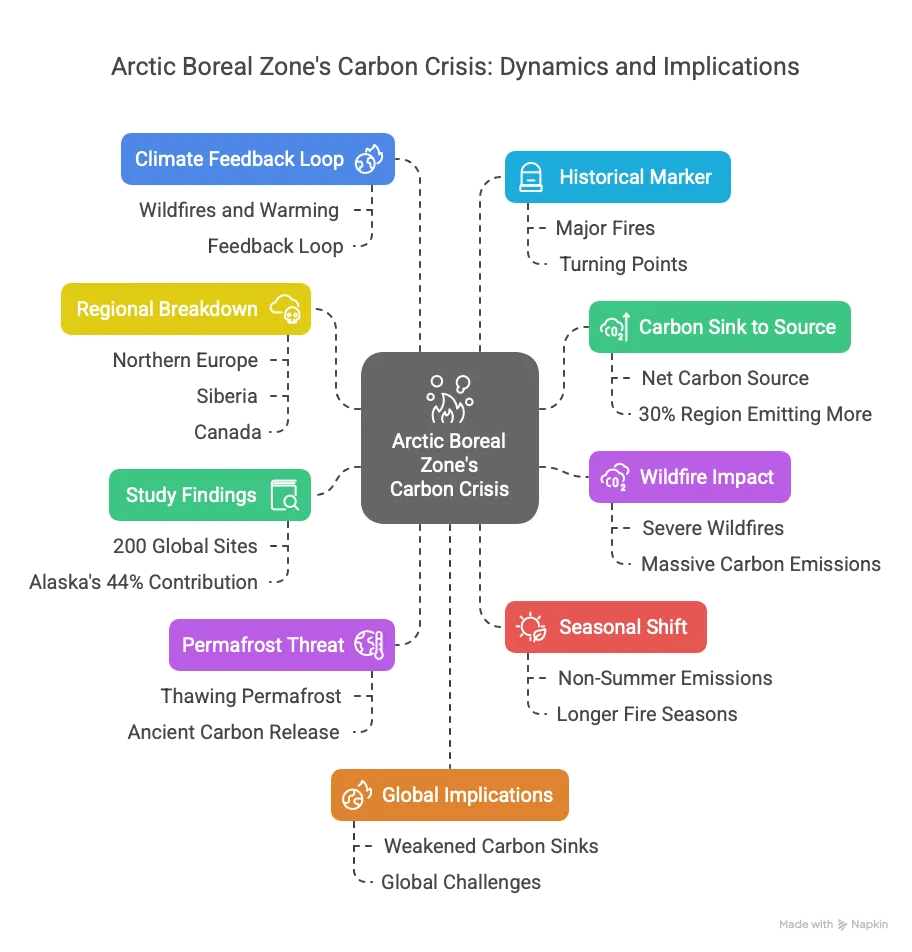
- Carbon Sink to Source: The Arctic Boreal Zone (ABZ), spanning tundra, forests, and wetlands, has shifted from a carbon sink to a source, with over 30% of the region now emitting more carbon dioxide than it absorbs.
- Wildfire Impact: Increasingly severe wildfires, fueled by climate change, are releasing massive carbon emissions, reversing the ABZ’s historic role as a carbon sequestering biome.
- Study Findings: Research from 1990-2020, using data from 200 global sites, shows that 30% of the ABZ became a net carbon source, with Alaska contributing 44% of new emissions.
- Permafrost Threat: Thawing permafrost, accelerated by fires, releases ancient carbon trapped for centuries, amplifying greenhouse gas emissions.
- Seasonal Shift: Carbon emissions during non-summer months (September-May) now exceed summer absorption (June-August), driven by longer fire seasons and microbial activity.
- Regional Breakdown: Northern Europe (25%), Siberia (13%), and Canada (19%) also contribute to the ABZ’s carbon emissions, highlighting a widespread issue.
- Climate Feedback Loop: Wildfires and warming create a feedback loop, where carbon release further accelerates global temperature rise.
- Historical Marker: The shift from sink to source likely began before 1990, with major fires in Eastern Siberia (2003) and Canada (2012) as turning points.
- Global Implications: The ABZ’s transformation weakens natural carbon sinks, posing challenges to global climate mitigation efforts.
- Monitoring Need: Experts stress the urgency of tracking these changes to predict and mitigate future climate impacts.
Glossary
- Arctic Boreal Zone (ABZ): A region around the Arctic Circle including tundra, coniferous forests, and wetlands, critical for carbon storage.
- Carbon Sink: An ecosystem that absorbs more carbon dioxide than it releases.
- Carbon Source: An area releasing more carbon dioxide than it absorbs.
- Permafrost: Permanently frozen ground storing ancient carbon, vulnerable to thawing.
- Greenhouse Gas: Gases like carbon dioxide that trap heat in the atmosphere, driving climate change.
Link o The Original Article – https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/wildfires-arctic-boreal-zone-carbon-sink-emissions/article69360974.ece